Table of Contents
Types of Payment Tokenization Formats Explained
1. Non-format Preserving Tokens:
Best Use Cases for Payment Tokenization
Tokenization vs. Encryption: What is the difference?
What are the Benefits of Payment Tokenization?
4. Improves Customer Experience:
How is Miden the Best Payment Tokenization Service provider in Africa?
At some point, you might have walked into a game center and been handed a set of colored chips—each one representing a specific cash value.
These chips aren’t mere objects; they serve as a secure and simplified substitute for real money, minimizing the risk of theft and making transactions smoother.
That is the idea behind payment tokenization.
This blog explores everything you need to know about payment tokenization, how it works, and why it matters.
If you’re also looking for a reliable token provider for your business, let me show you why Miden is the best option for you.
What is Payment Tokenization?
Payment Tokenization is the process of replacing sensitive information with a randomly generated string of characters or symbols, i.e, tokens, to reduce the likelihood of fraud or breach.
In this case, the sensitive information, typically Primary Account Numbers (PANs), is stored in a PCI-compliant token vault by the token creator - it can be an entity, payment processor, etc.
When it comes to online sales, the customers’ credit card details are replaced with randomly generated characters (tokens) to ensure a safe transaction. To the extent that if the merchant or any other person accessed the card details, they wouldn't be able to use it because it doesn't contain the real payment details.
Since payment tokenization can’t be reverse-engineered, this method is an effective strategy in protecting the users' details and ensuring safe payment transactions.
Types of Payment Tokenization Formats Explained
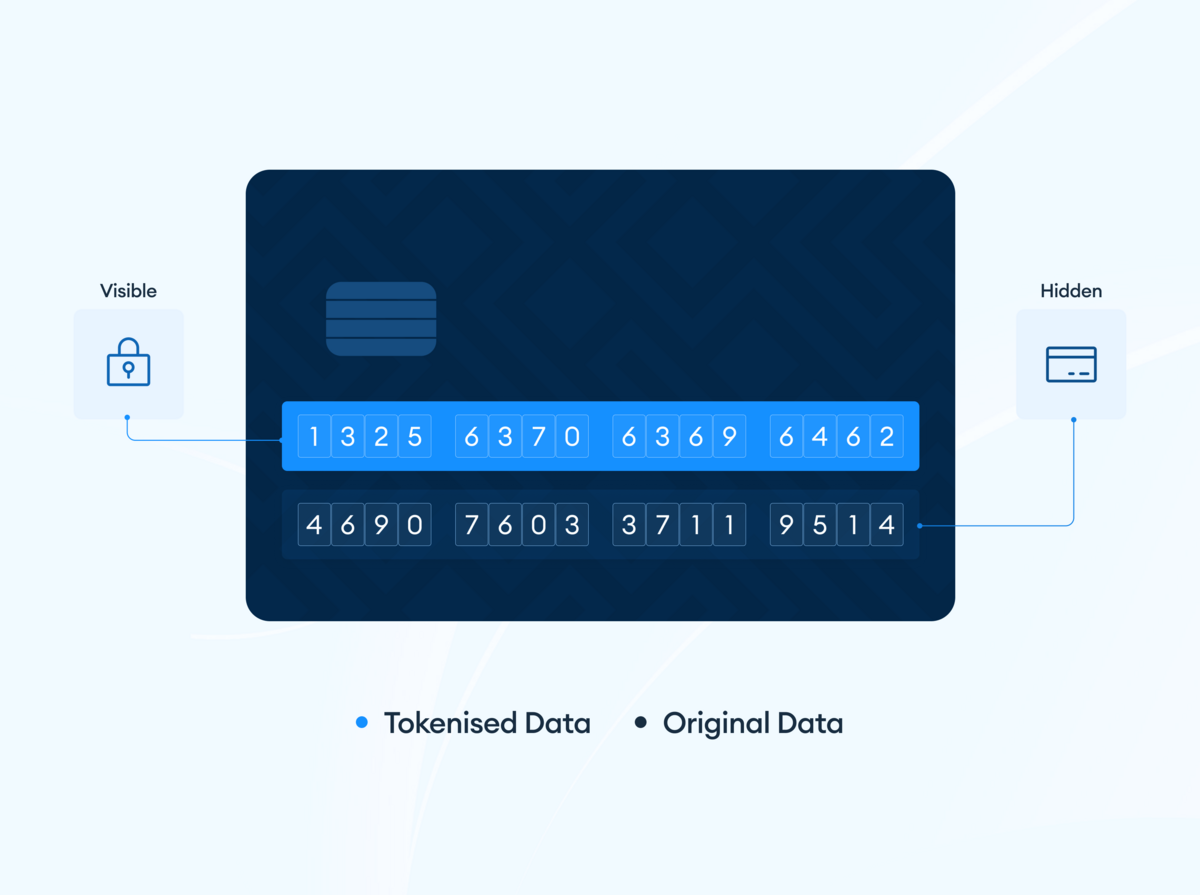

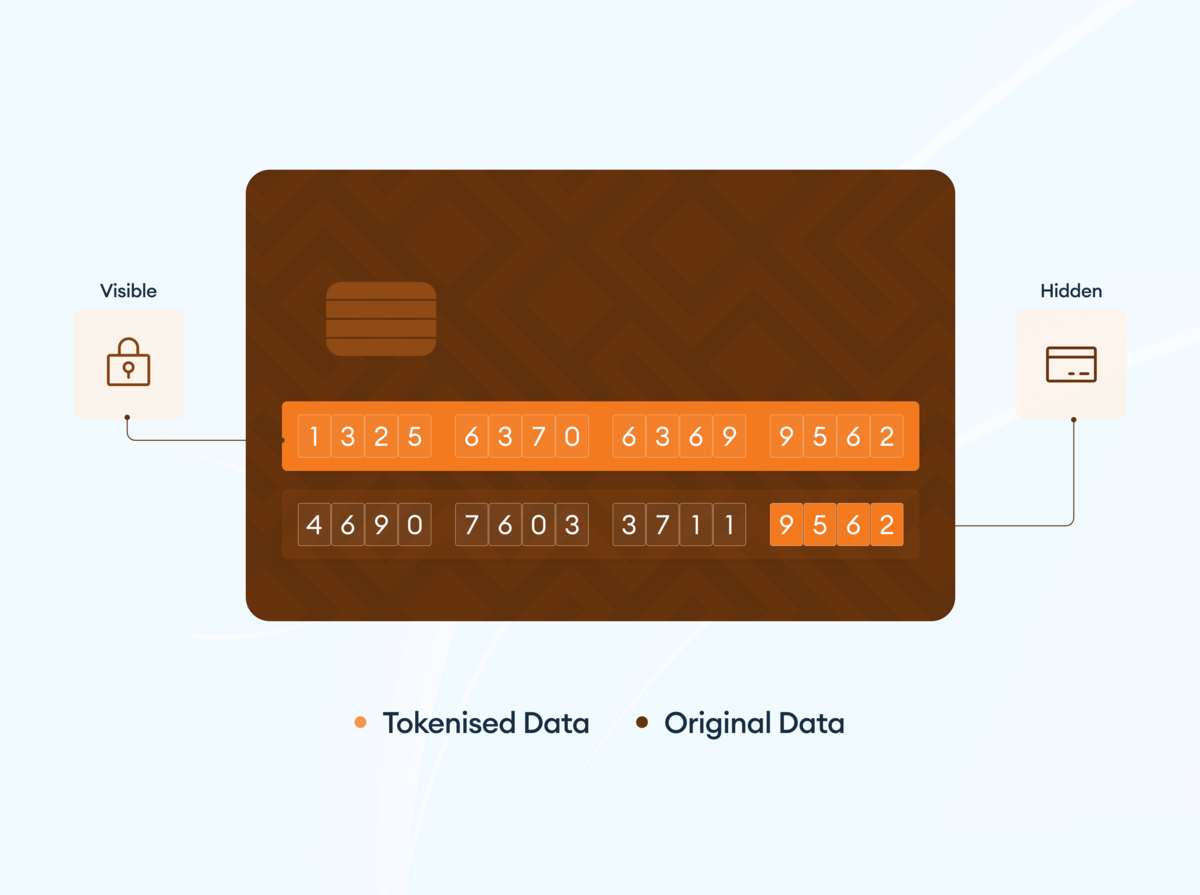
Payment tokens can be in different forms, including;
1. Non-format Preserving Tokens:
A non-format-preserving token typically doesn’t appear like its original data. For example, a nine-digit Social Security number (SSN) could be replaced with a six-digit numerical and non-numeric characters, such as [D1T!@2].
2. Format Preserving Tokens:
A format-preserving token maintains the same format as the original sensitive information but merely scrambles the digits. For example, a credit card number of ‘1234 5678 9123 4567’ could be ‘3219 6745 8675 4312’.
3. Selective Masking Tokens:
This form of payment token partially changes the value of the original information. Adopting a hybrid approach, a selective masking token leaves some of the values unchanged, typically for verification purposes. For example, a credit card number of ‘1234 5678 9123 4567’ can be ‘3737 2221 4539 4567’ or ‘DSGW SWWD OM1W 4567’.
Other payment token formats can also be designed specifically for single/multiple use, a device, or a merchant.
Best Use Cases for Payment Tokenization
Here are some of the cases where payment tokenization can be implemented;
- E-commerce Retailers: These are companies that offer goods and services in an e-commerce store, such as WordPress, Shopify, or more. Tokenization helps to ensure your customers' data is secured and stored according to compliance regulations.
- Subscription-based Companies/Retailers: These are entities that enable recurring billings to ensure that the customers’ payment data for recurring purchases is well-protected from fraudulent activities.
- Brick-and-mortar Retailers: Tokenization also assists physical store owners who use a digital payment system, such as point-of-sale (POS) systems or mobile banking platforms, to ensure that their customers' details are secured.
- Embedded Finance Companies: Tokenization helps these companies ensure that their embedded payment infrastructure does not store customers' information.
Tokenization vs. Encryption: What is the difference?
Tokenization and encryption are two related concepts and are typically directed to the same goal, i.e, to comply with the PCI DSS compliance regulations. However, each concept utilizes different strategies.
If sensitive information is encrypted rather than tokenized, the information could be decrypted. In essence, tokenization replaces sensitive information with unique characters that are not directly related to the replaced information, whereas encryption transforms the sensitive data into an unreadable form.
What are the Benefits of Payment Tokenization?
1. Improved Security:
Tokenization helps to improve security by ensuring that users’ information is not exposed to data breaches or fraud. This creates a safe system for payment processing for each user.
2. Ensure PCI DSS Compliance:
By ensuring cardholders’ information is secured, businesses will ensure adherence to the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). According to the Verizon report, between 2014 to 2019, companies that complied fully with PCI DSS never experienced data breaches. Plus, 53% of companies that experienced breaches confirmed that they were noncompliant at that time.
3. Cost-effectivism:
Tokenization reduces data breaches, thereby cutting costs, which a merchant will most likely spend on compliance strategies. Plus, when a merchant’s security details are breached, they get to pay numerous fees such as legal fees, fines, and more. Tokenization helps to minimise such cost.
4. Improves Customer Experience:
Tokenization improves customers' experience by increasing loyalty and seamless payment transactions. When payment processes are secured, customers are more likely to trust the system and the company (issuer) itself. For example, a survey has shown that about 78% of users will stop digital payments with a brand if the company experiences a breach.
How is Miden the Best Payment Tokenization Service provider in Africa?
Miden stands out as one of the top payment tokenization service providers for financial and non-financial companies across Africa. With over 500 thousand virtual cards issued, Miden ensures optimal compliance with the industry standards of the Payment Card Industry (PCI).
They assist companies to streamline their payment infrastructure within a few days to weeks, rather than the traditional six to twelve months standard.
Additionally, Miden is PCI DSS certified for secure card processing and NDPR‑compliant for data privacy needs. With Miden, all customers’ sensitive information is heavily protected and stored securely in a vault.
Boasting more than 99.9% uptime, Miden serves major fintechs, travel companies, e‑commerce firms, and more, looking for a seamless payment infrastructure for their consumers in or outside Africa.
Bottom Line on ‘The Basics of Payment Tokenizations’
Payment tokenization provides a safe and effective strategy to protect users' payment information from merchants, hackers, or other third parties.
It ensures that the users’ details are not kept in the merchant file, thereby building trust and improving customer experience.
In this blog, we explored everything about payment tokenization, from its meaning to the process and benefits. We also highlighted Miden as the best provider of a safe and secure tokenized system for your company.
Ready to launch your own branded virtual cards in weeks, not months? Join the fastest-growing payment tokenization provider in Africa.





